Copepod IDs
This page will compile a visual guide to the species we’ve collected, including photographs and notes on identification. This is a work-in-progress example for the calanoid copepods of Lake Champlain - we could consider something similar.
The information below is a guide to some of the features that might be useful for quickly identifying copepods in Pomeranian Lake district and other regions. This information was compiled by Maria Hołyńska.
Cyclopoids
Cyclops scutifer
0.9‒1.6 mm; spine formula 3.4.3.3; pediger 4 and 5 with lateral wings; P4 coxal seta usually swollen; P4 enp3, apical spines very different in length; caudal rami short (l/w: 4.0‒5.0) and pilose; insertion of caudal seta II > 1/3 ramus length; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Cyclops vicinus
1.3‒2.3 mm; spine formula 2.3.3.3; pediger 4 and 5 with lateral wings; caudal rami long and pilose; insertion of caudal seta II < 1/3 ramus length; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Cyclops kolensis
1.0‒1.3 mm; spine formula 2.3.3.3; pediger 4 and 5 without lateral wings; caudal rami short (l/w: 4.0‒5.0) and pilose; insertion of caudal seta II < 1/3 ramus length; P5. [Koźmiński 1933]
Megacyclops viridis
1.2‒2.1 mm; A1 short, not reaching beyond cephalothorax; spine formula 2.3.3.3; P4 enp3 apical spines subequal; caudal seta V long; caudal rami short and pilose; caudal seta VI / caudal seta III >2; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Megacyclops gigas
2.0‒3.5 mm; A1 short, not reaching beyond cephalothorax; spine formula 2.3.3.3; caudal seta V long; P4 enp3 apical spines subequal; caudal rami long and pilose; caudal seta VI / caudal seta III <2; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Macrocyclops albidus
1.7‒2,5 mm; A1 beyond cephalothorax; A1 last segment with smooth hyaline membrane; spine formula 3.4.4.3; P4 enp3 apical spines subequal; caudal rami very short and medially naked; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Macrocyclops fuscus
1.8‒2.4 mm, A1 beyond cephalothorax; A1 last segment, coarse dents on hyaline membrane; spine formula 3.4.4.3; caudal rami very short medially pilose; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Acanthocyclops trajani
1.1‒1.6 mm; A1 not reaching beyond cephalothorax; spine formula 3.4.4.4; caudal seta V long; caudal rami length/width 4.0‒6.0, medially naked. [Mirabdullayev & Defaye, 2002]
Mesocyclops leuckarti
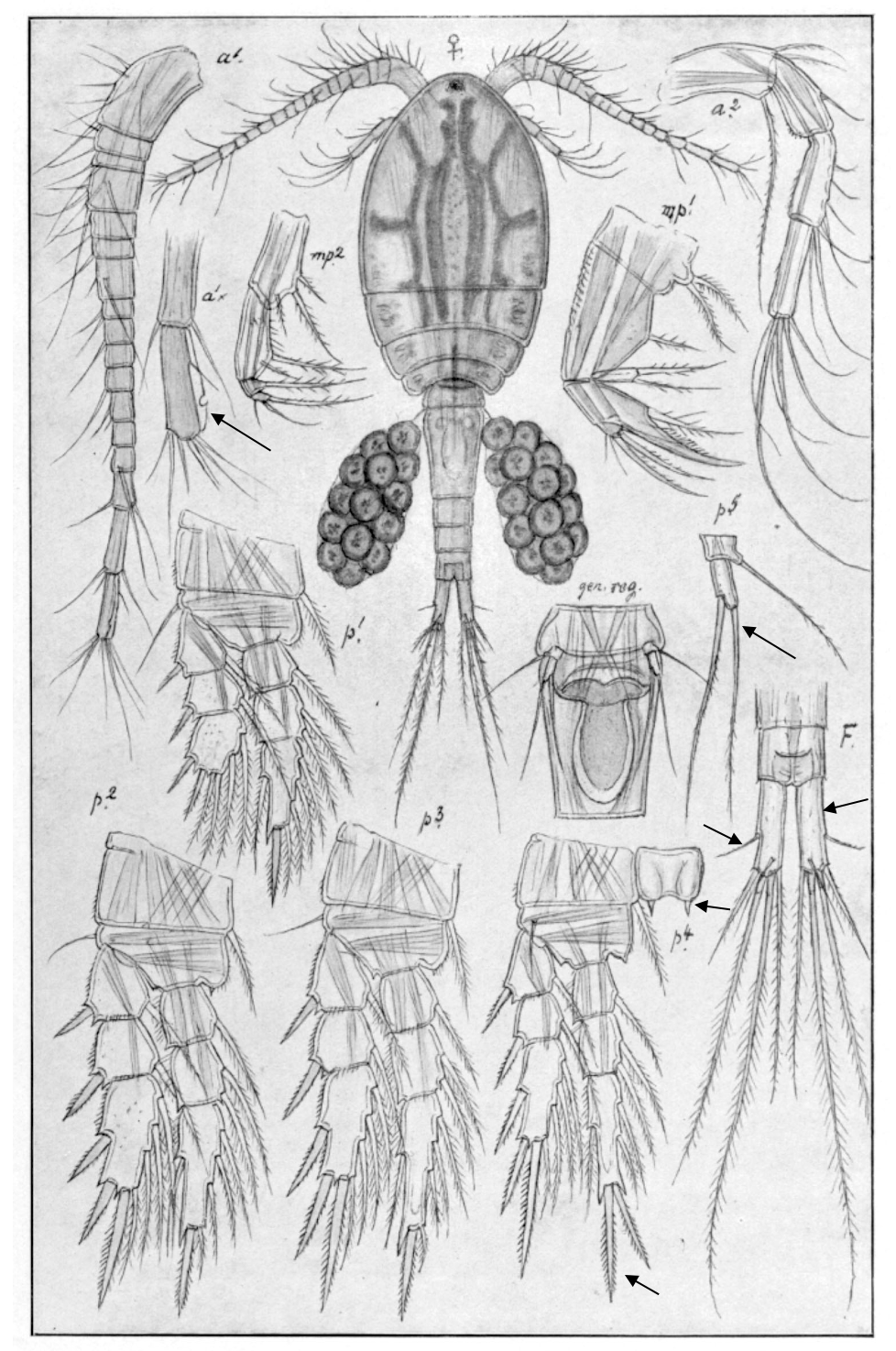
0.9‒1.5 mm; A1 17th (last) segment, hyaline membrane with notch; caudal rami short, lateral seta long; spine formula 2.3.3.3; P4 enp3 apical spines subequal; P4 coupler with acute outgrowth; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Thermocyclops crassus
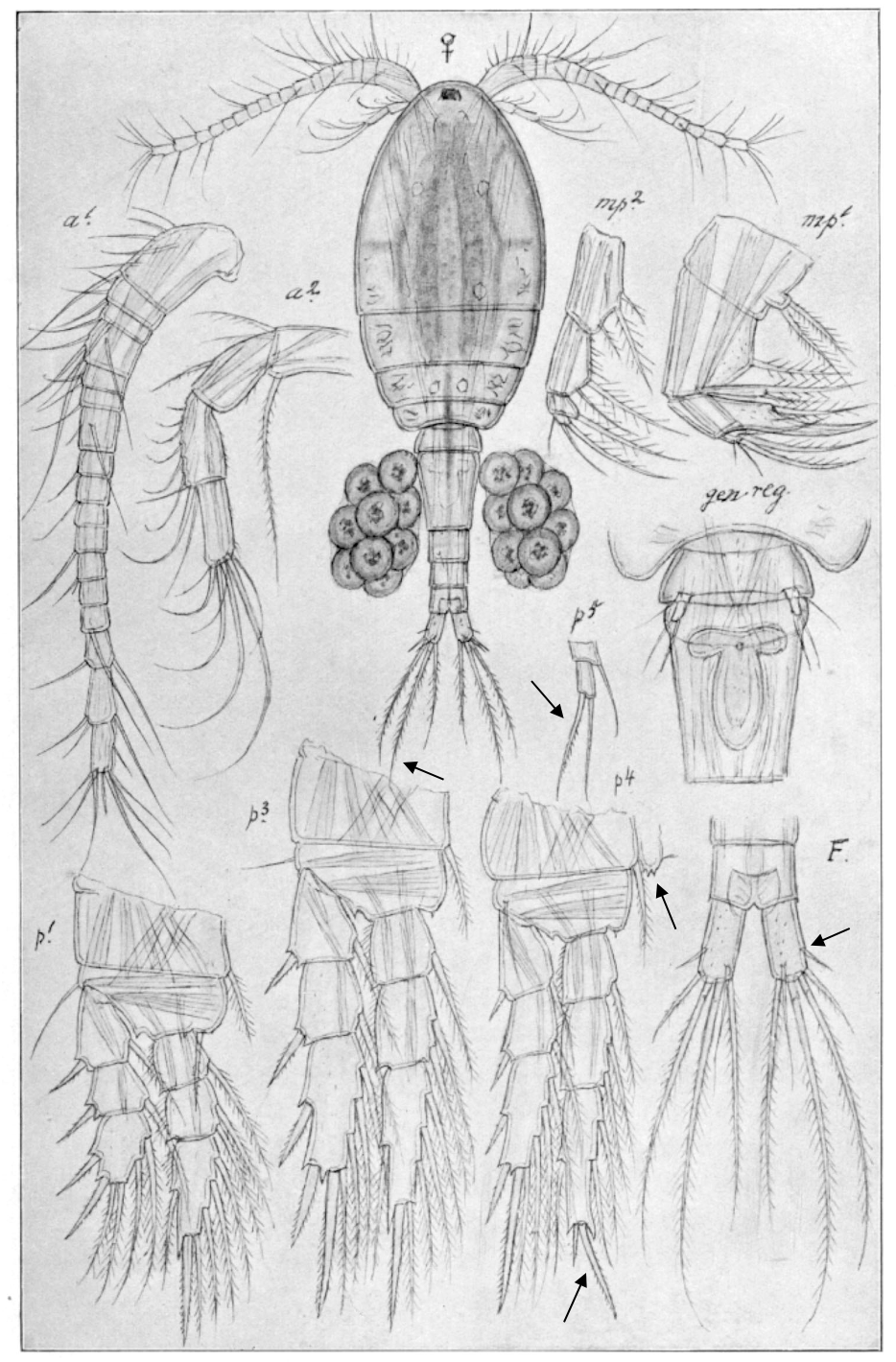
0.9‒1.1 mm; caudal rami short; caudal seta V short and with curly tip; spine formula 2.3.3.3; P4 enp3 apical spines, in/out ca 2.0; P4 coupler with obtuse outgrowths bearing spinules; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Diacyclops bicuspidatus
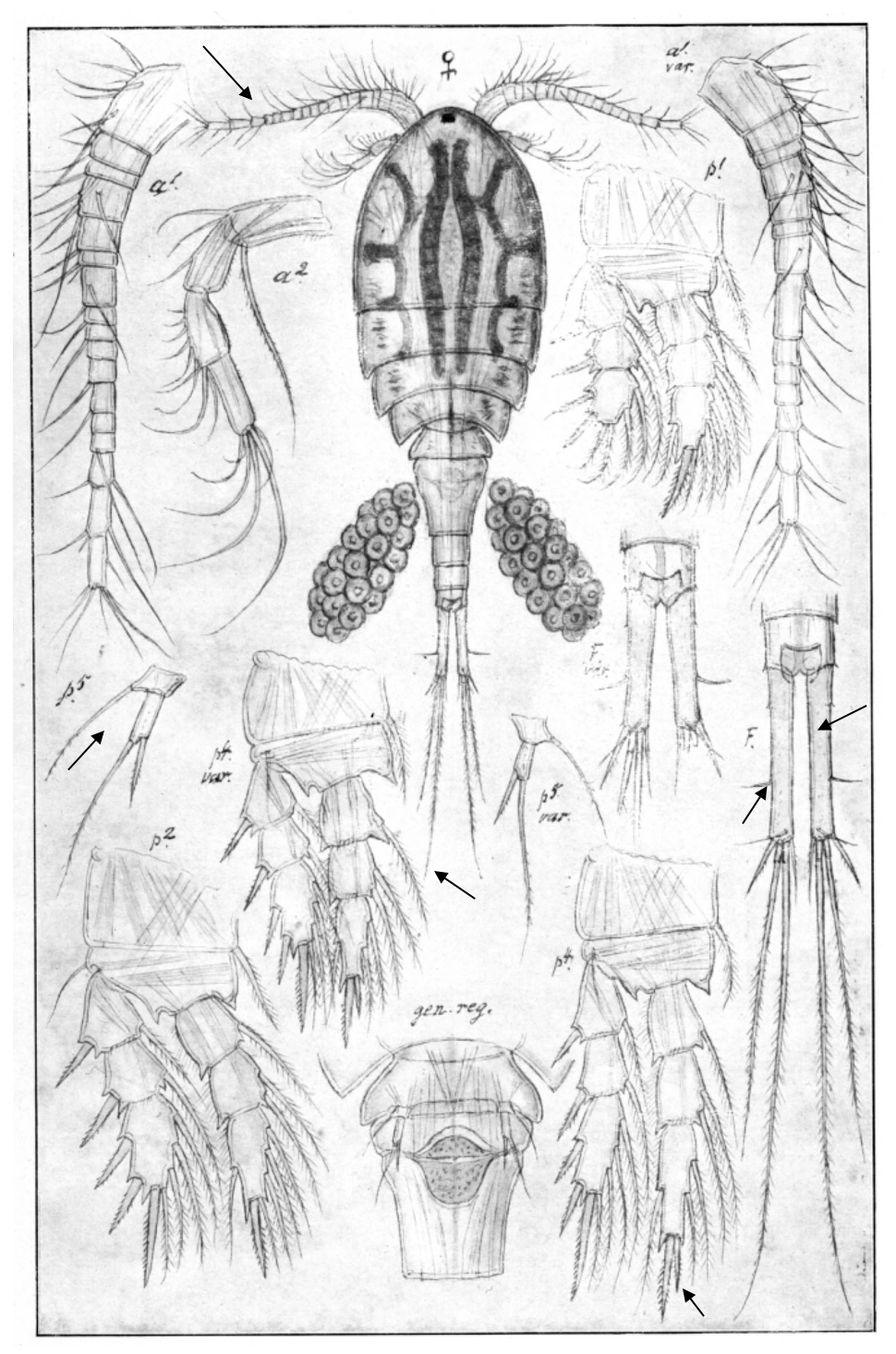
0.8‒1.6 mm; A1 not reaching beyond cephalothorax; caudal rami long, seta II (lateral) inserted at posterior 1/3; caudal seta V long; spine formula 2.3.3.3; P4 enp3, of apical spines inner one shorter; P4 coupler without outgrowths; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Thermocyclops oithonoides
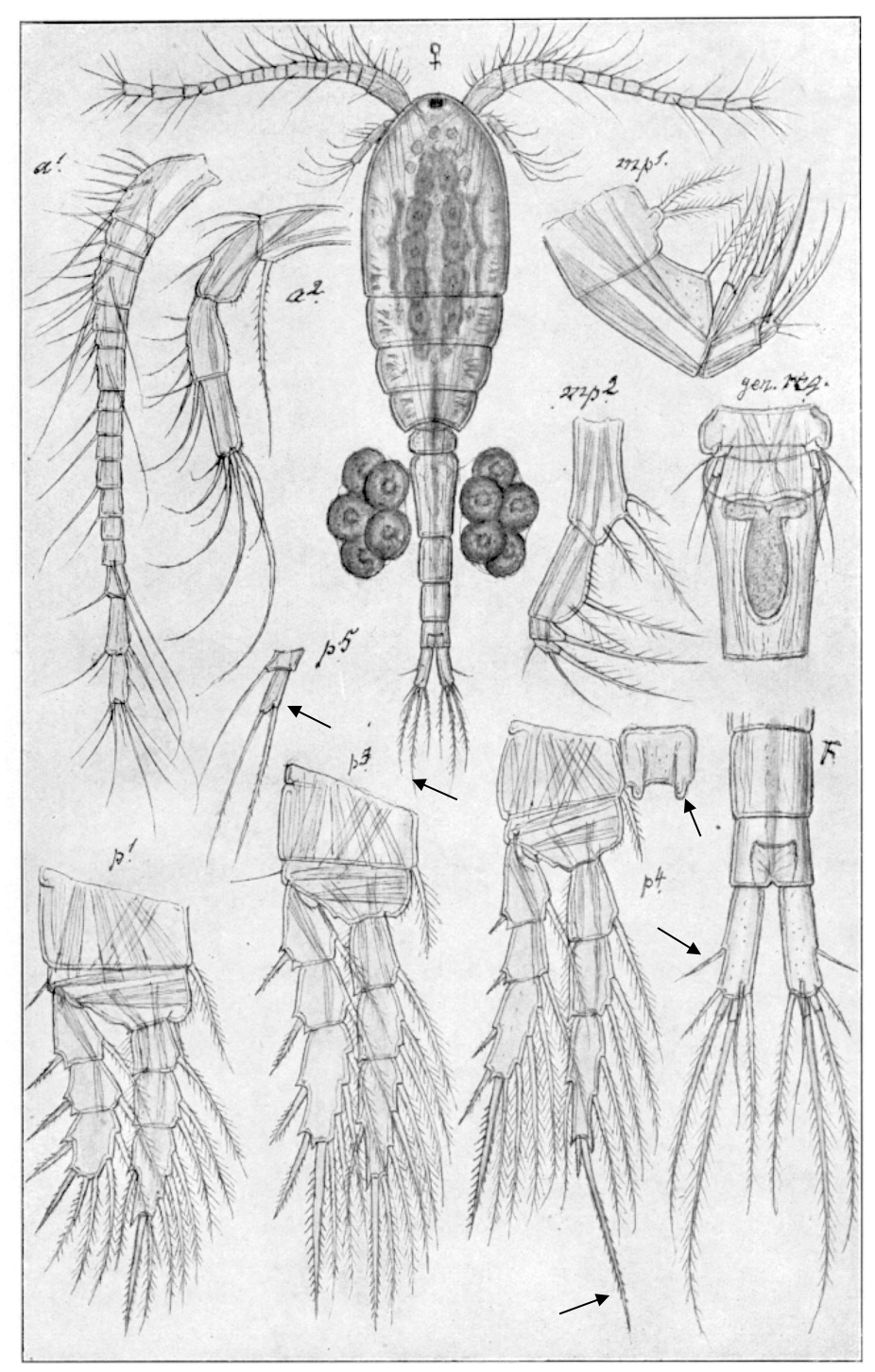
0.8‒1.0 mm; caudal rami short, caudal seta II (lateral) long; caudal seta V short, tip not curling; spine formula 2.3.3.3; P4 enp3 apical spines, in/out ca 3.0‒4.0; P4 coupler with high outgrowths bearing spinules; P5. [Sars 1914-1918]
Calanoids
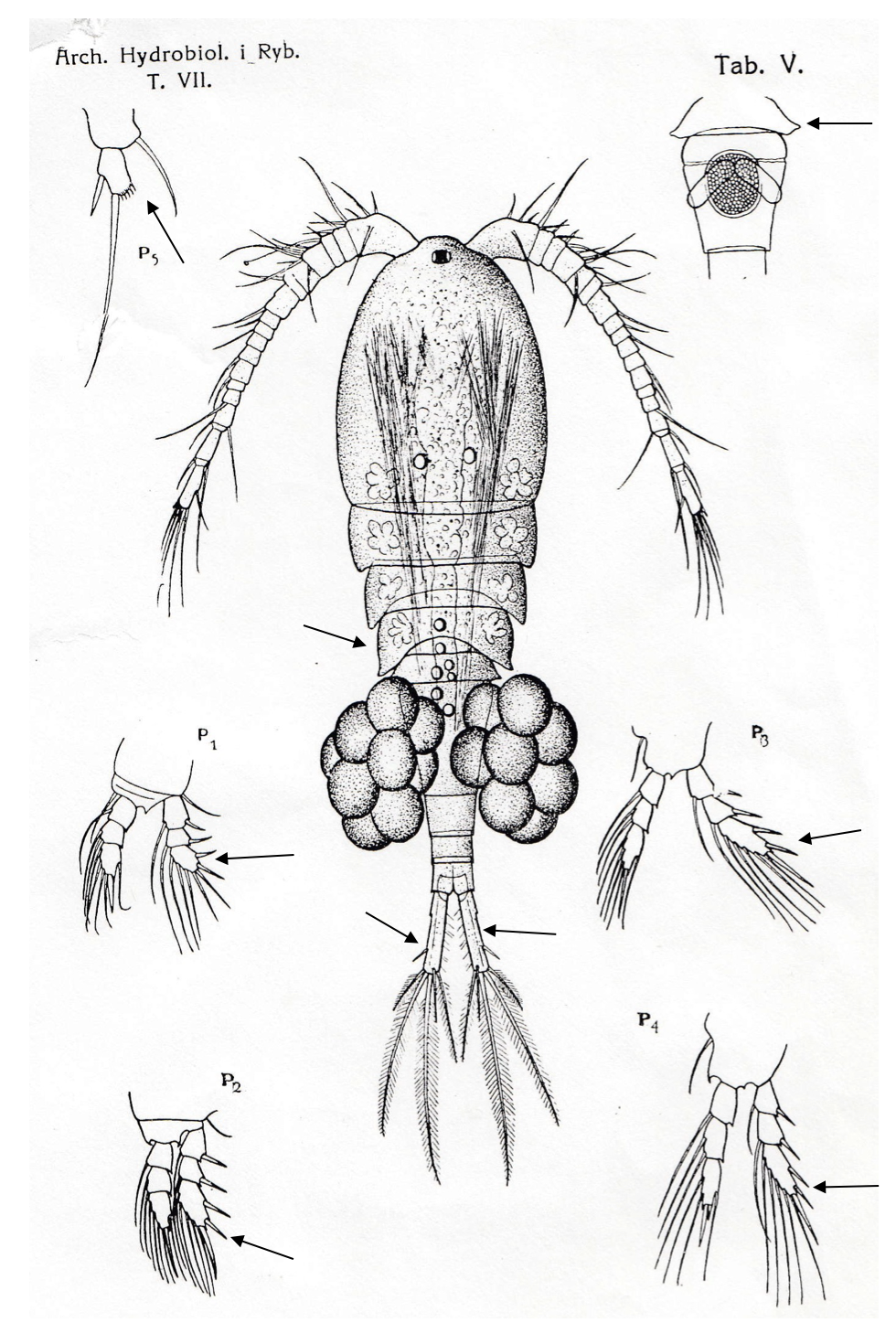
Limnocalanus macrurus
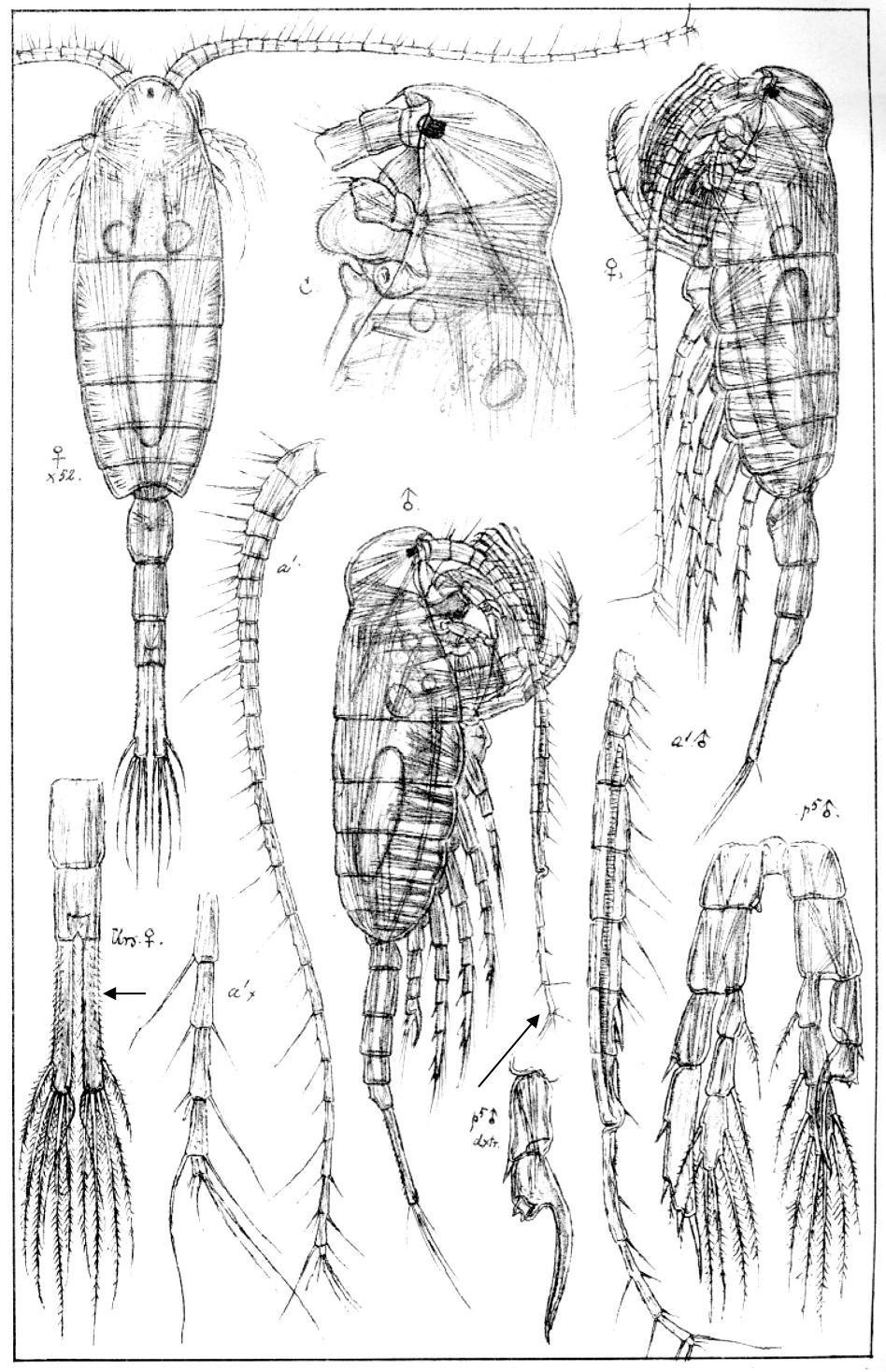
2.0‒3.0 mm, P1‒P4 enp three-segmented, caudal rami long, both lateral and medial margin pilose; antennule reaching beyond prosome. [Sars 1914-1918]
Heterocope appendiculata
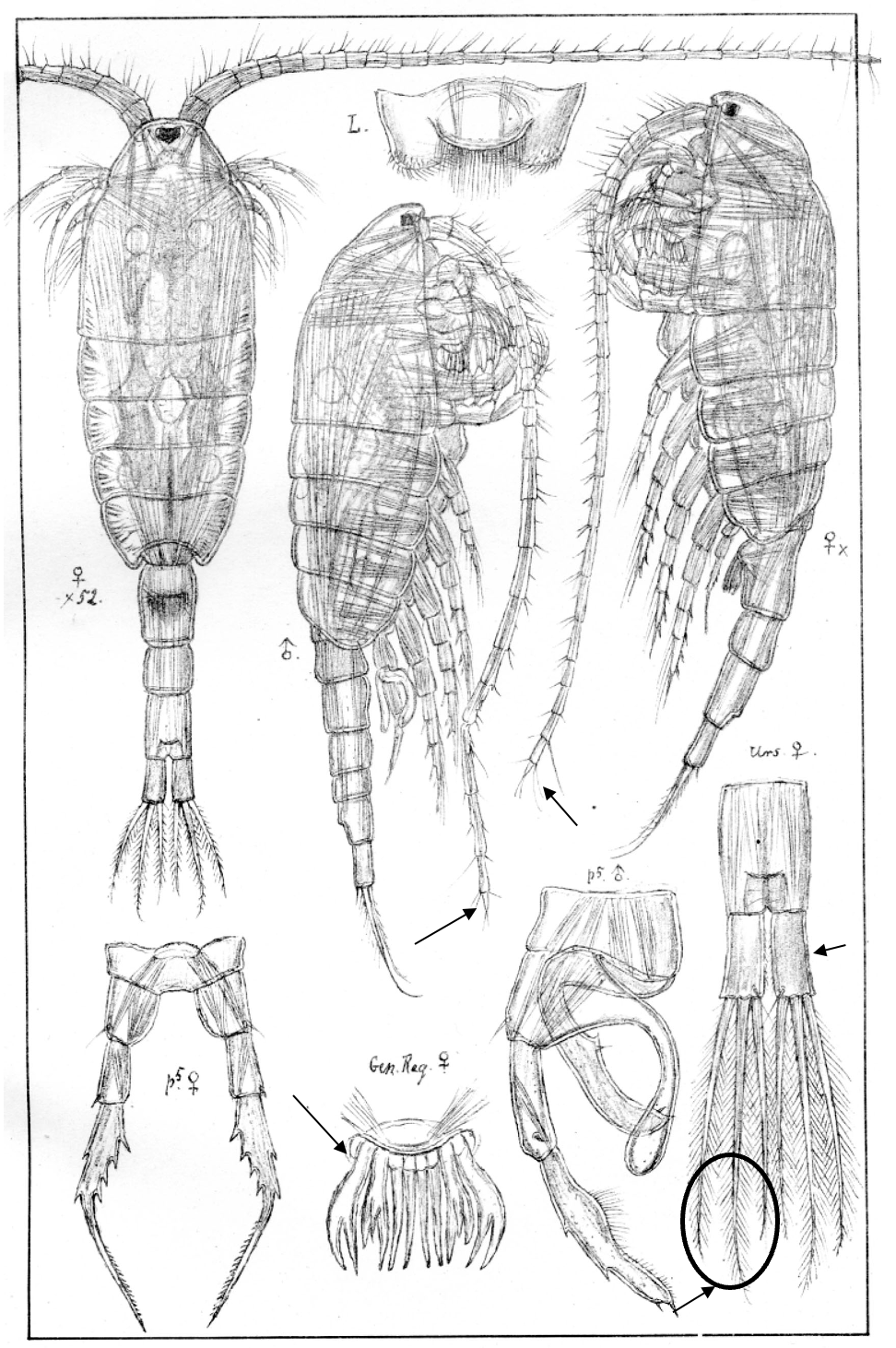
2.0‒2.2 mm; caudal rami short with 3-3 terminal setae; P1‒P4 enp one-segmented; female genital plate with finger-like lobes; antennule reaching beyond caudal rami. [Sars 1914-1918]
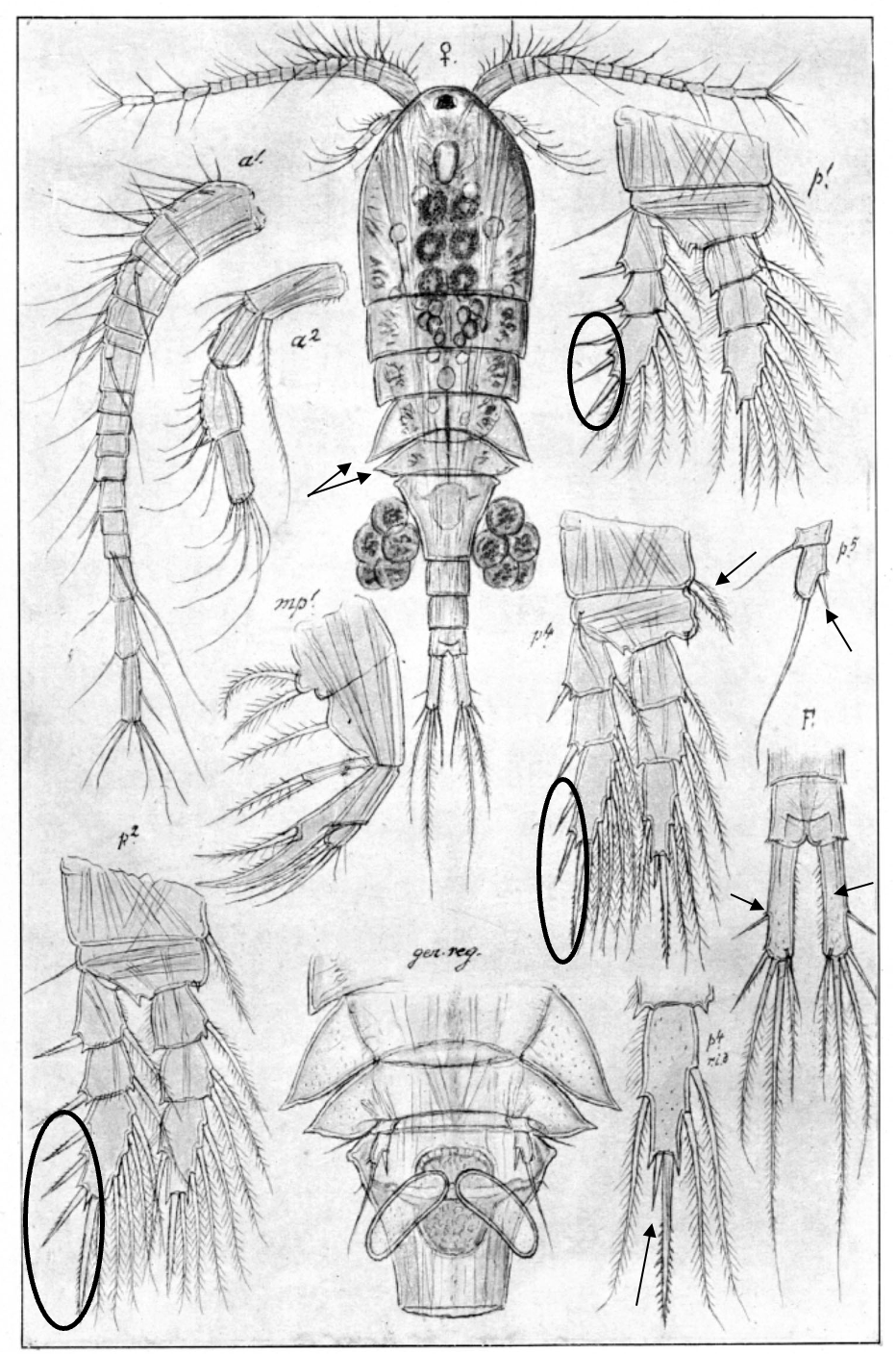
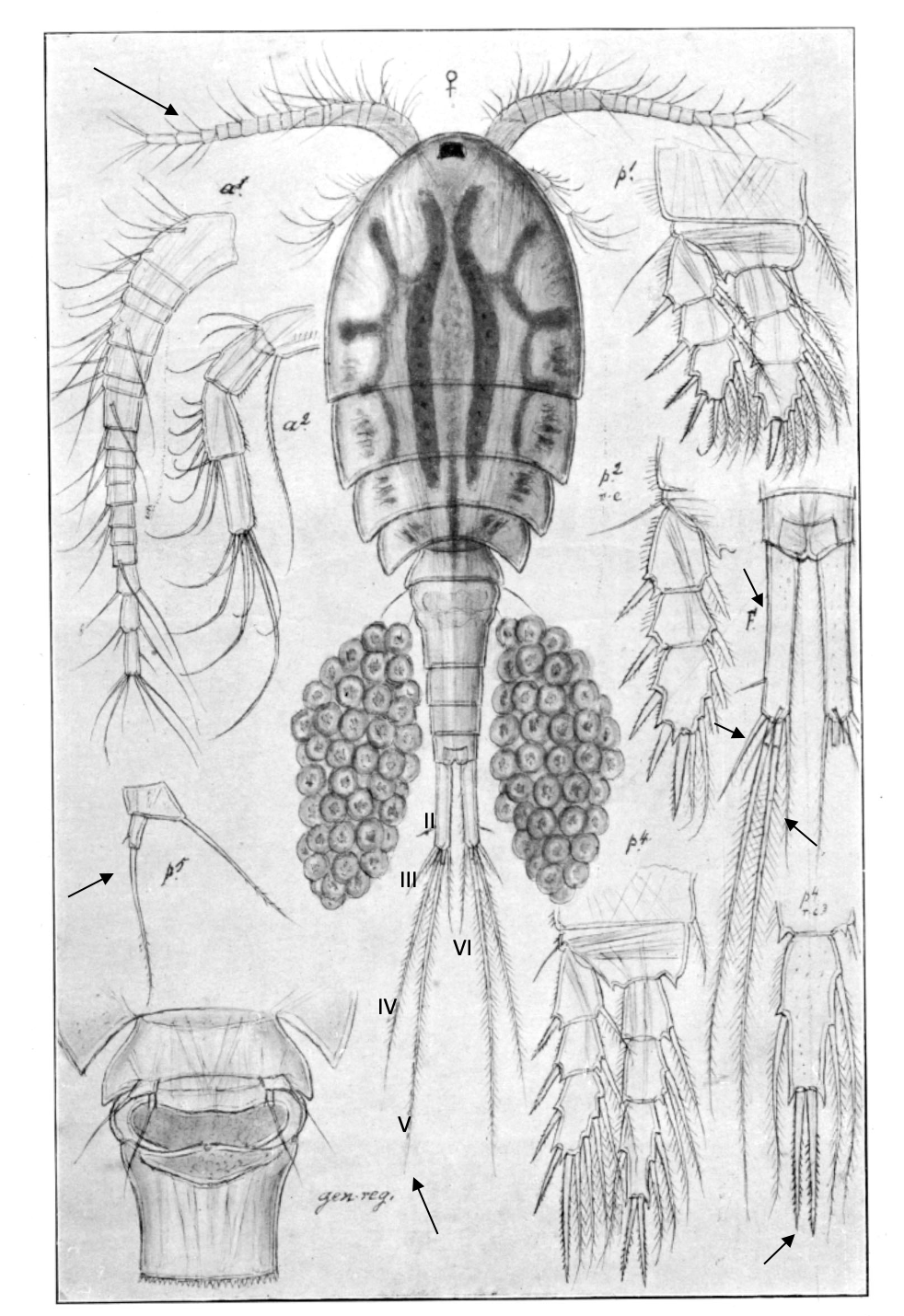
Eurytemora velox
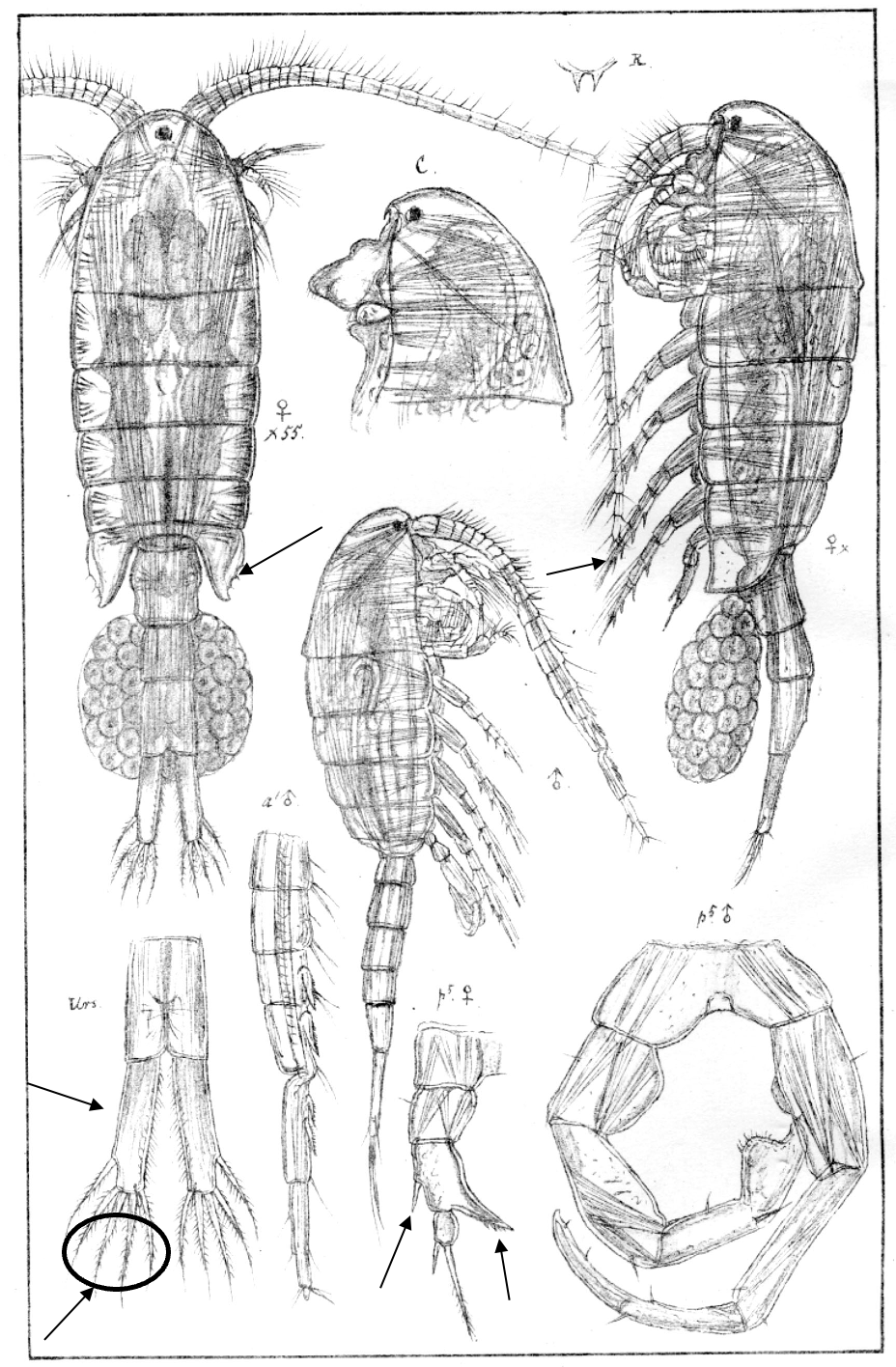
1.3‒2.2 mm; P2‒P4 enp two-segmented; A1 reaching posterior end of prosome; caudal rami long with 4 terminal setae; female pediger 5, lateral wings broad/irregular shape; female P5: exp1 with 1 lateral spine, and inner outgrowth posteriorly directed. [Sars 1914-1918]
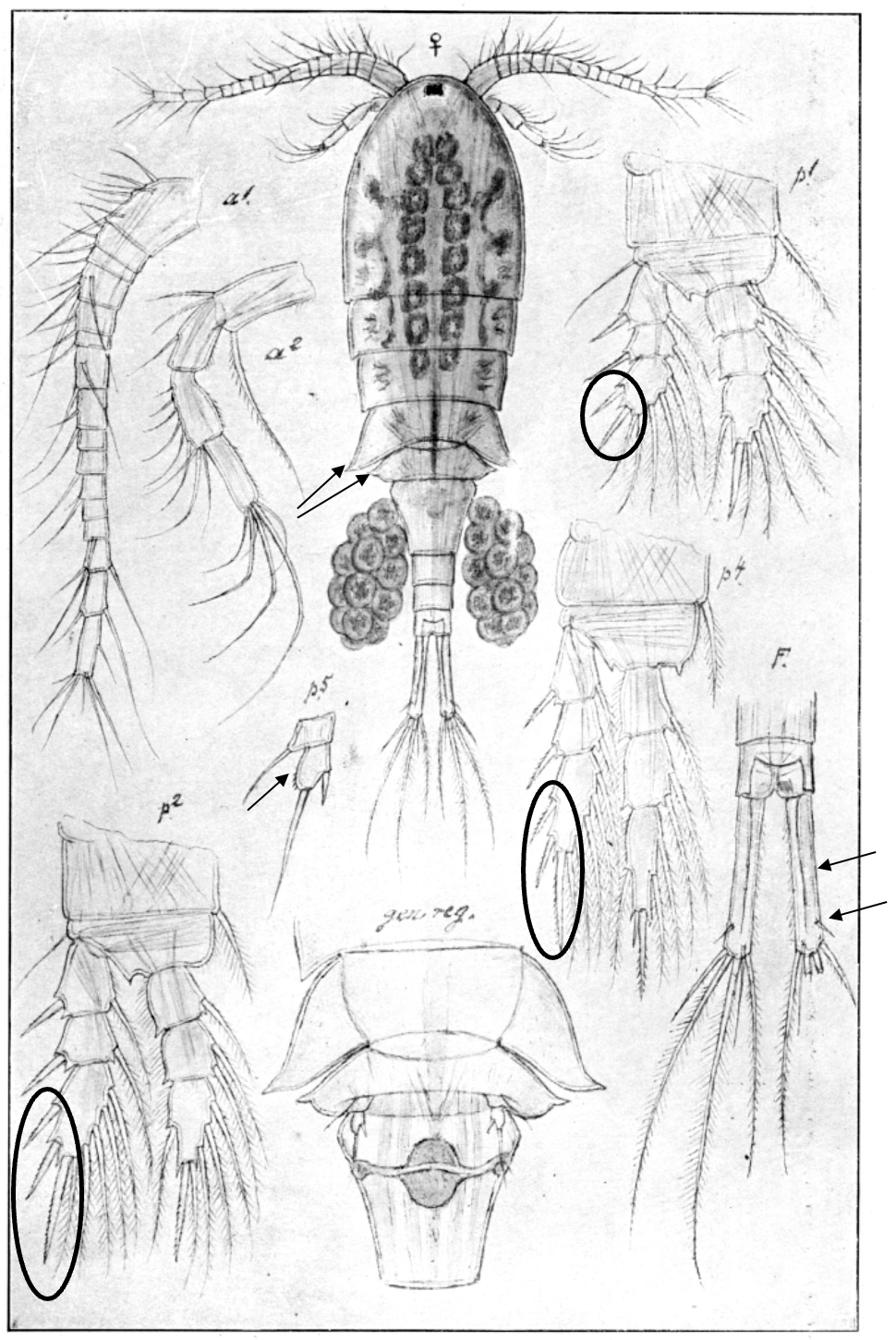
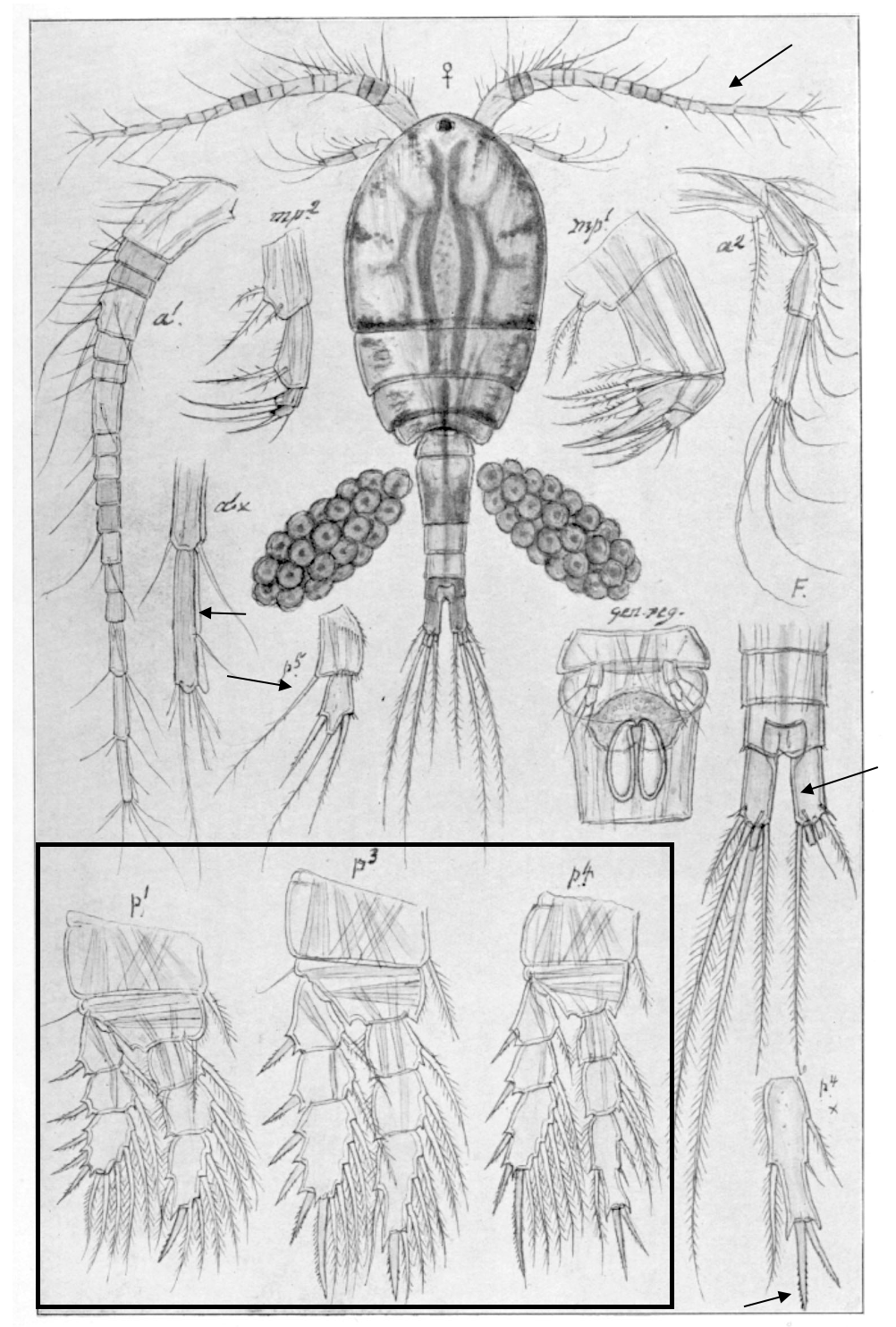
Eurytemora lacustris
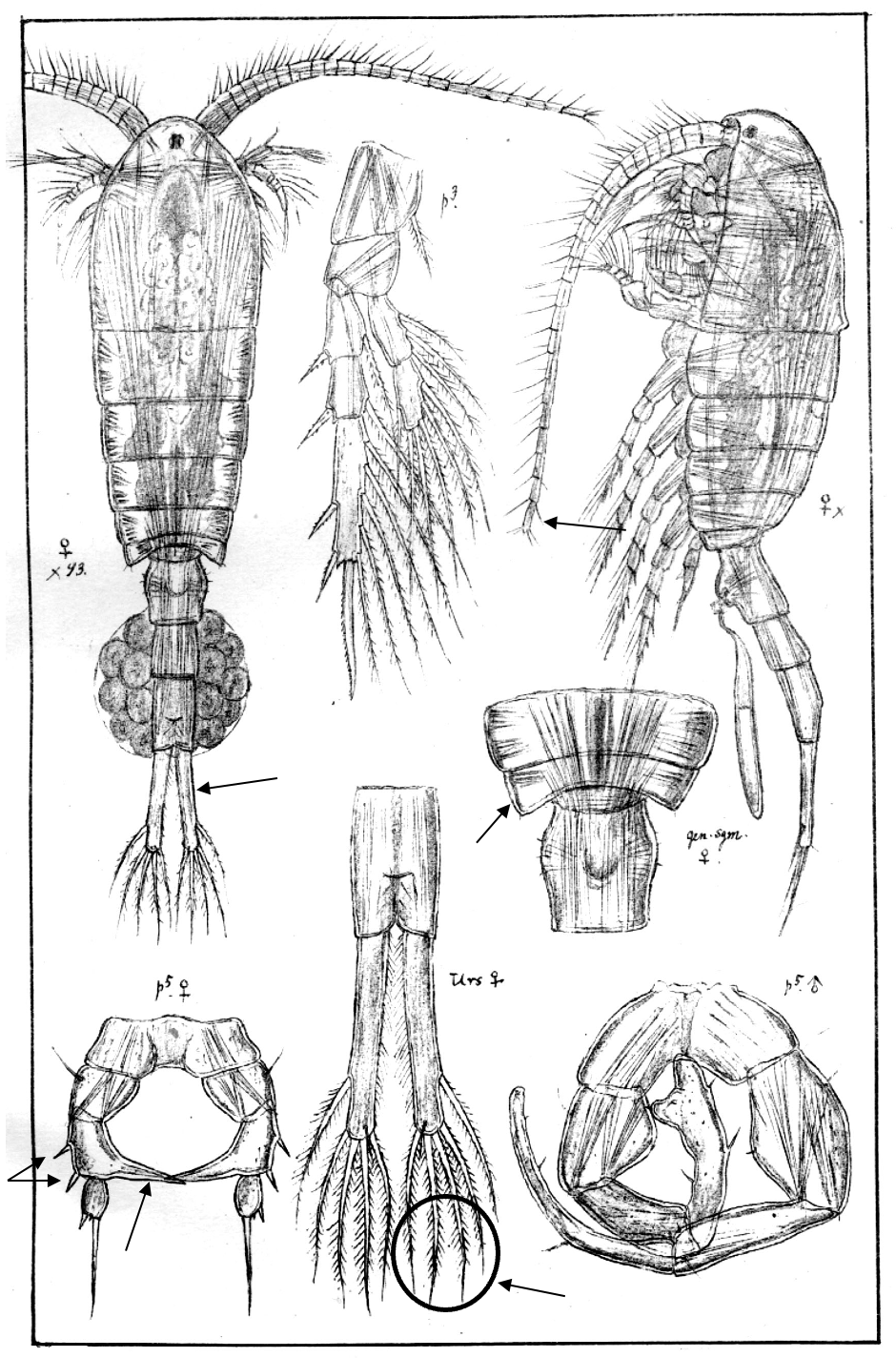
1.0‒1.5 mm; A1 reaching posterior end of prosome; P2‒P4 enp two-segmented; caudal rami long, with 4 terminal setae; female, pediger 5 without lateral wings; female P5, exp1 with 2 lateral spines, and inner outgrowth medially directed. [Sars 1914-1918]
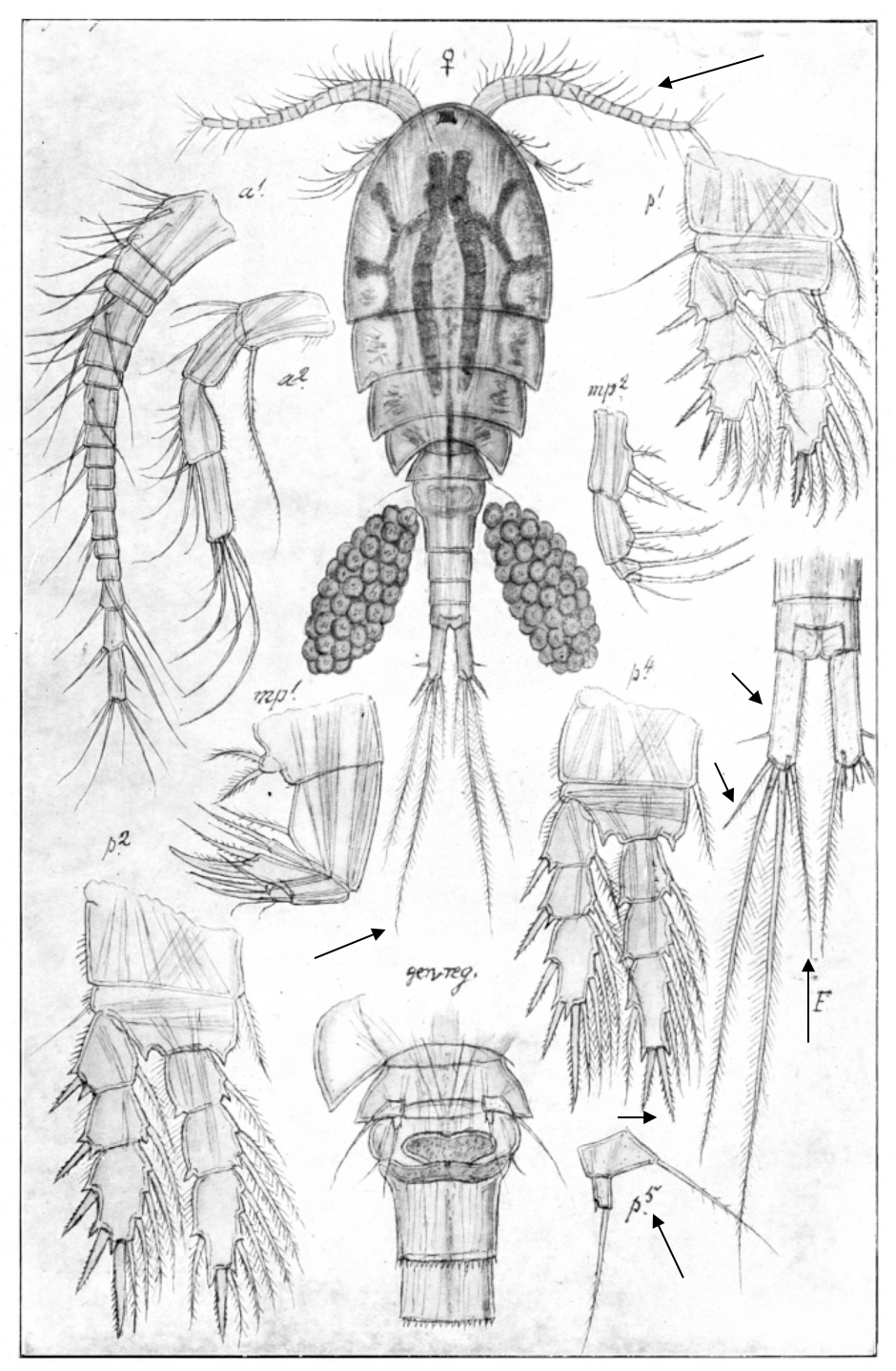
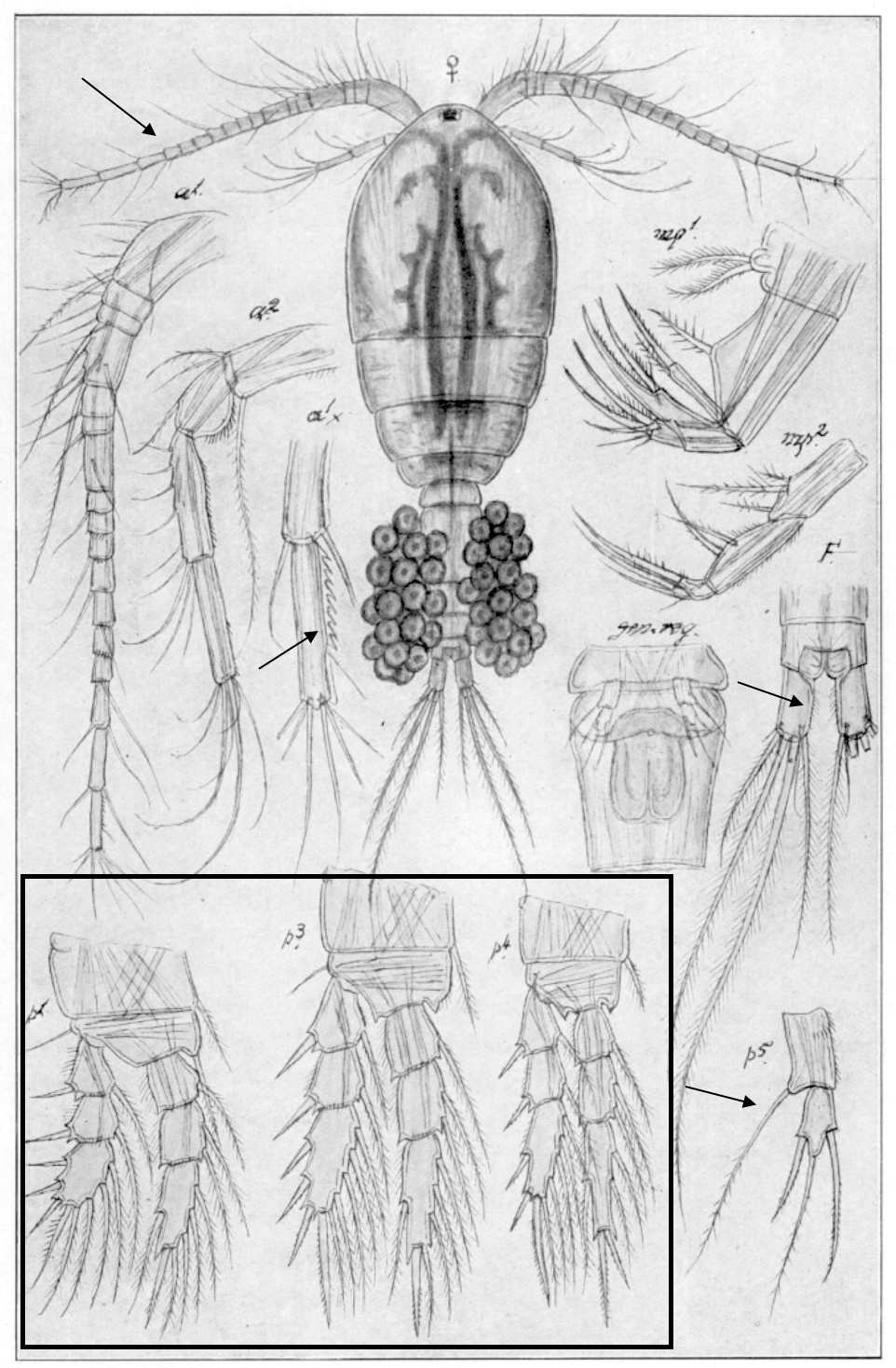
Eurytemora carolleeae
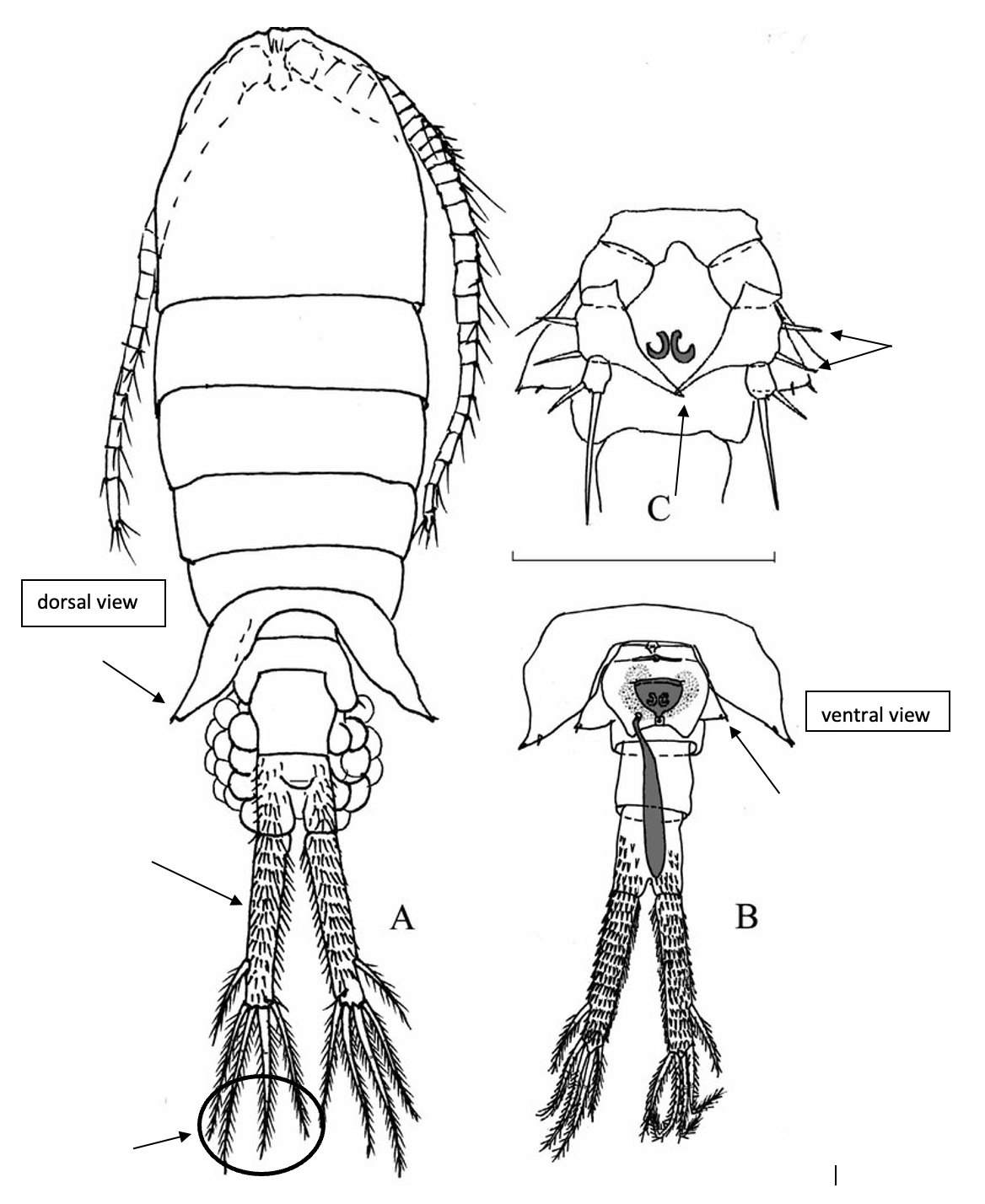
ca 1.2 mm; P2‒P4 enp two-segmented; caudal rami long, with 4 terminal setae; female pediger 5, lateral wings triangular, posteriorly directed; female genital somite with wing-like outgrowth; female P5, exp1 with 2 lateral spines, and inner outgrowth posteriorly directed. [Alekseev & Souissi 2011]
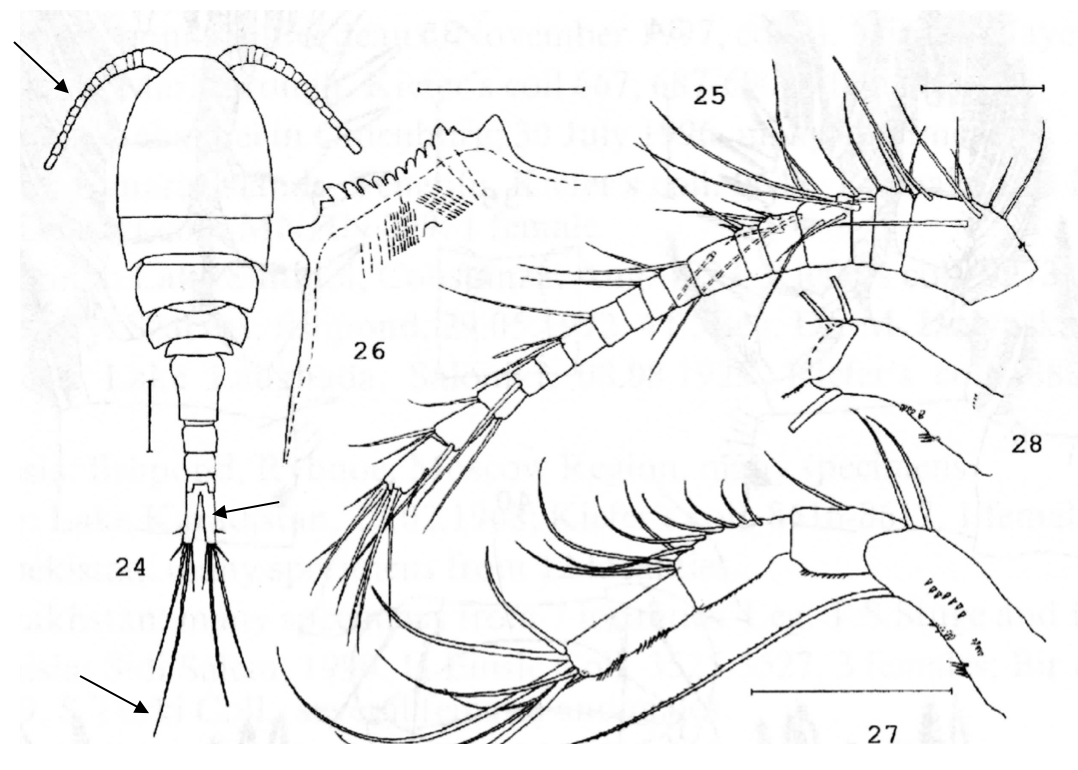
Additional notes on Eurytemora species
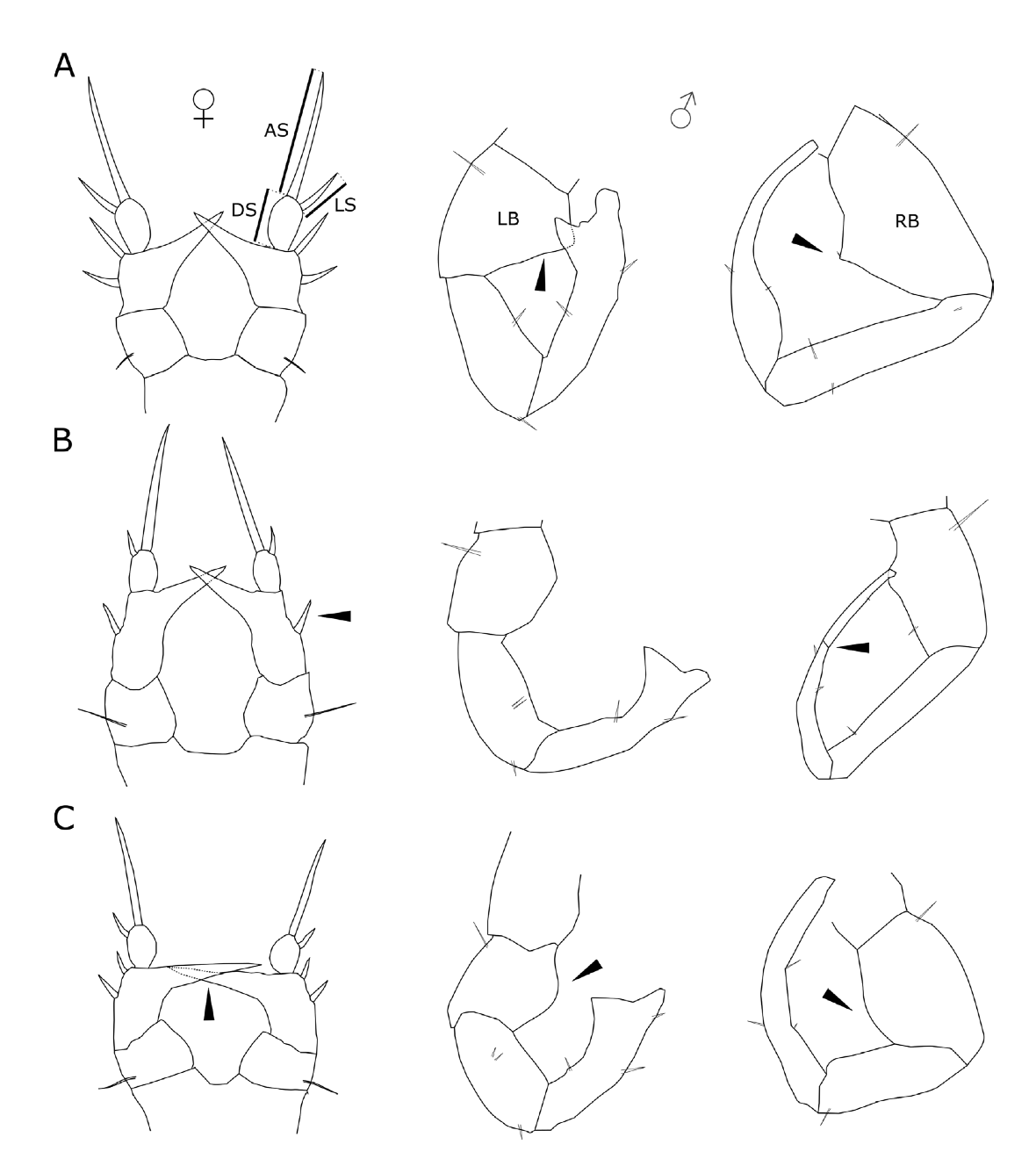
Fifth pair of legs of related Eurytemora species (A) E. affinis(B) E. velox(C) E. lacustris. Abbreviations: AS – apical seta, DS – distal segment, LS – lateral spine, LB – left basipod, RB – right basipod. Arrows indicate important characteristics of fifth pair of legs. [Sługocki et al 2019]
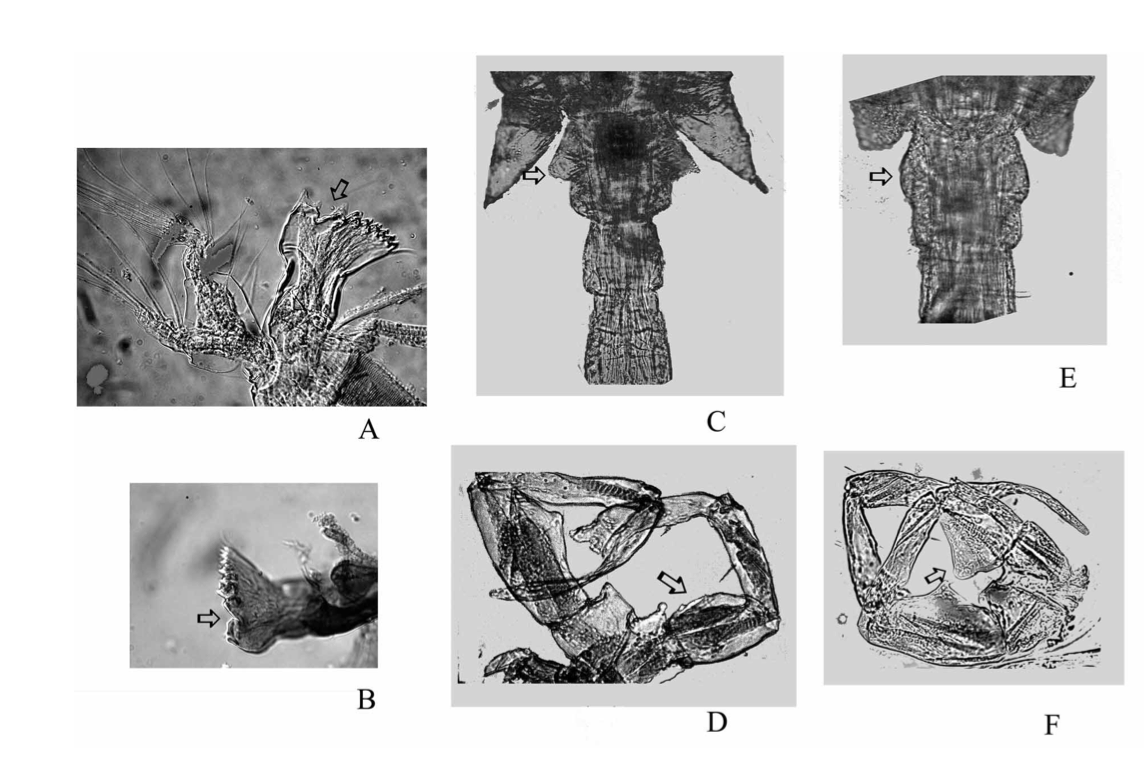
Eurytemora carolleeae sp. nov. (A–D) and E. affinis (Poppe, 1880) (E–F): A, female mandible, arrow indicating a gap; B, male mandible, arrow indicating a gap; C, female genital somite with wing-like outgrowth; D, male leg 5 with arrow indicating left basipod; E, female genital somite without wing-like outgrowth; F, male P5, arrow indicating left basipod. (Photo: Mrs Natalia Sukhikh) [Alekseev & Souissi 2011]
Eudiaptomus graciloides
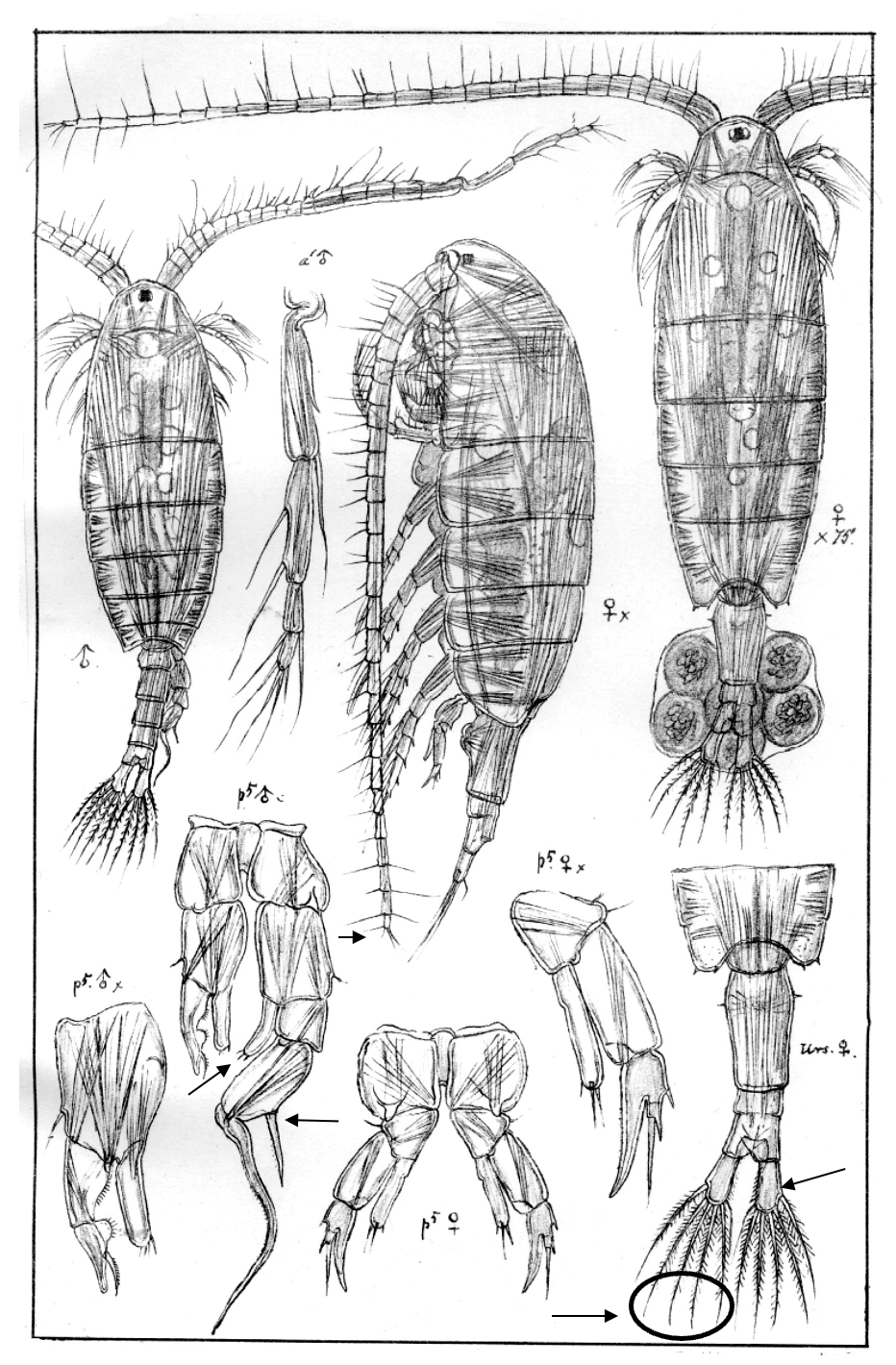
1.0‒1.5 mm; P2‒P4 enp three-segmented; caudal rami short, with 4 terminal setae; antennule reaching beyond caudal rami; male, right P5: enp slender, and exp2 lateral spine in distal half of segment. [Sars 1914-1918]
Eudiaptomus gracilis
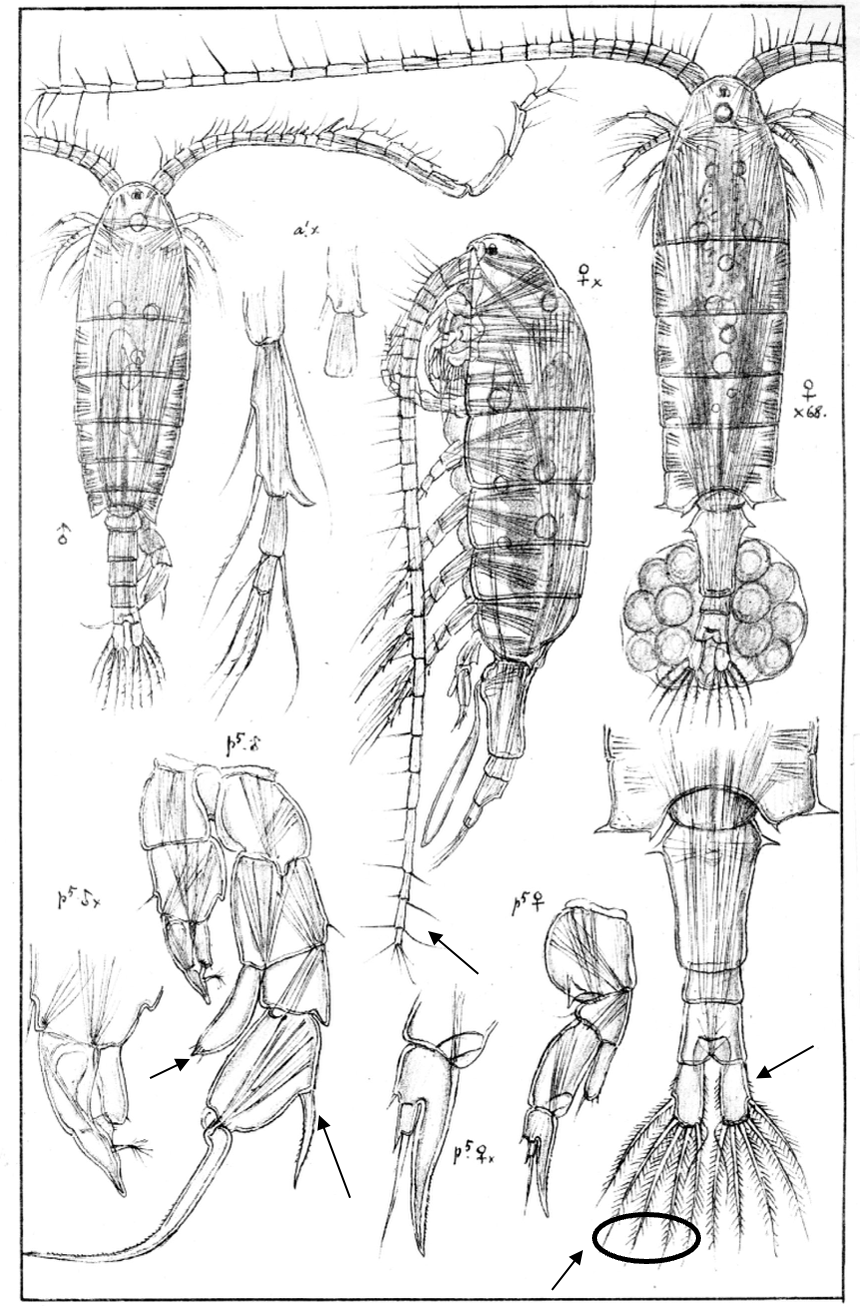
1.0‒2.0 mm; P2‒P4 enp three-segmented; caudal rami short, with 4 terminal setae; antennule beyond caudal rami; male, right P5: enp large, and exp2 lateral spine in proximal half/middle of segment. [Sars 1914- 1918]